Sunday, November 16, 2008
Vocab, summary, and concept check for 8.4
Carbon cycle: It's the process that inorganic carbon moves to organic.
Greenhouse effect: atmospheric gases trap heat close to Earth's surface and prevent it from escaping into space
Summary
Tiny chloraplast and mithocondria can effect in earth scale, and one is carbon cycle. It's the cycle that carbon moves from inorganic to organic compound. For example, sunlight's inorganic carbon dioxide goes to plant, and consumers consume producers like plant. Both consumer and producers returns the carbon dioxide.
In cabon cycle, carbon dioxide takes big parts of it. Most of organisms gives out cabon dioxide a little , except plants. When it gets to the total effect of earth atmosphere, it gives huge effect.
In our atmosphere, carbon dioxide takes0.03 percent of it. This carbon dioxide traps heat and refelct it to the earth, so that earth's temperature increases about 10 celcius.
Concept check
1. Example of move of inorganic to organic carbon is the when sunlight changes into the plant's carbon dioxide
Example of organic to inorganic carbon is when consumer have eaten the producer and breathed out carbon
2. Carbon dioxide takes big parts in our atmosphere, because it controlls the amount of heat coming by it's thickness
Wednesday, November 12, 2008
Summary and concept check for 8.3

2.
Wednesday, October 8, 2008
vocab list
Organelle: part of cell with a specific function
Plasma membrane:Thin outer boundary of a cell that regulates the traffic of chemicals between the cell and it's surroundings.
Nucleus:It is an atom, the central core that contains protons and neutrons in a cell.
Cytoplasm:region of a cell between the nucleus and t he plasma membrane.
Cell wall:Strong wall outside a plant cell's plasma membrane that protects the cell and maintains it's shape.
Prokaryotic cell: Cell lacking a nucleus and most other organells.
Eukaryotic cell: Cell with a nucleus and other internal organells
Diffusion: net movement of the particles of a substance from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated.
Equilibrium: point at which the number of diffusing molecules moving in one direction is equal to the number moving in the opposite direction.
electively permeable membrane: membrane that allows some substances to pass more easily than others and blocks the passage of some substances altogether.
Tuesday, September 9, 2008
The chapter 5 review questions
a. cellulose b. sucrose c. water d. testosterone
Answer: C. water
2. Which of the following terms includes all the other terms on this list?a. polysaccharide b. carbohydrate c. monosaccharide d. glycogen
Answer: B. Carbohydrate
3. Which term is most appropriate to describe a molecule that dissolves easily in water? a. hydrocarbon b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. organic
Answer: C. Hydrophilic
4. Cholesterol is an example of what kind of molecule?a. protein b. lipid c. amino acid d. carbohydrate
Answer: B. Lipid
5. The 20 amino acids vary only in their a. carboxyl groups. b. side groups .c. amino groups. d. lipid groups.
Answer: C. Amino groups
6. A specific reactant an enzyme acts upon is called the a. catalyst. b. sucrase. c. active site. d. substrate.
Answer: a. Catalyst
7. An enzyme does which of the following?
a. adds heat to a reaction, speeding it up b. lowers the activation energy of a reaction c. cools a reaction, slowing it down d. raises the activation energy of a reaction
Answer: D. Raise the activation energy of a reaction
Short Answer8. Besides satisfying your hunger, why else might you consume a big bowl of pasta the night before a race?
9. How are glucose, sucrose, and starch related?
They are all used as energy for a animal. and plants.
10. What are steroids? Describe two functions they have in cells.
One of function is hydrophobic, circulates our body in our body as
chemical signals.
11. How are polypeptides related to proteins?
Both are made out of amino acid
12. How does denaturation affect the ability of a protein to function?
Saturday, September 6, 2008
summary 5.3
lipid: Definition - One of class of water- avoiding compounds.
Property:It act as a boundary that surrounds and contains the aqueous contents of your cell.
Hydrophobic:water avoiding compounds.
Fat:Organic compound consisting of a three carbon backbone attached to the three fatty acids.
statured fat: It's a fat in which all three fatty acid chains the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms.
Unstatured fat: It's a fat with less than the maximum number of hydrogens in one or more of its fatty acid chains .
Diet: If there is many unstatured fats included in your diet, it's unhealthy.
Steroid:lipid molecule with four fused carbon rings.
It's hydrophobic.
some steroids circulate our body as chemical signal.
Cholesterol: It's the best know steroid and it's an essential molecule found in the memberanes that surrounds our cell
concept check
1.What is property does lipid share?
Lipids act as a boundary that surrounds and contains the aqueous contents of your cells.
2.What are the parts of fat molecule?
Saturated fat and unsaturated fat.
3.Describe two ways that steroids differents from fat
Differ from function and structure, such as fat circulates our body as chemical signal
4.what does unsaturated fat on a food label?
Those are the things mainly made out of vegetables.
Monday, September 1, 2008
Summary 5.1
Organic molecule:
Inorganic molecule:
- Definition : just opposite of organic molecule(non carbon-based molecule)
- Examples: Water(H2O),Oxygen(O2),Ammonia(NH3)
- Definition:It's the bond between only carbon and hydrogens.
- It's worldwidely used important fuel,such as Methane the fuel used to heat up home.Hydrogen and Nitrogen are frequently found in organic molecules.
- Examples:Methane(CH4)
Functional group:
- Definition: It's a group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecule.
- Some of the functional groups are important in the chemistry of life
- The carbon skeleton and the attached functional group determine the properties of an organic molecule
Hydrophilic:
- Definitions:It means attract water molecules
- Most organic molecules that contain hydroxyl groups are hydrophilic.
Monomers:
- Definition:Small molecular unit that is the building block of a larger molecule
Polymers:
- Definition:Long chain of small molecular units
- It's a straight chain of monomers,much as a train is a string of many individual cars.
- Every living cell has thousands of different kind of polymers.
- When monomer is added to a chain, a water molecule is released.
Concept check5.1
 2.Connection between polymers and monomers is that polymers connect monomers in straight line.
2.Connection between polymers and monomers is that polymers connect monomers in straight line.3.A water molecule, dehydration reaction.
4.

Thursday, August 28, 2008
Summary of 5.2: Carbohydrates pe fuel and builduing material



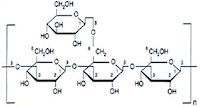

Carbohydrate(CH2O) is an organic compound made upoif sugar molecules.
Monosaccharides:It's the simple sugars contains just one sugar unit, and glucose,fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides.(names of the sugar has ~ose in last)
Disaccharides:It constructed by cell, when dehydraton reaction happens. The most common disaccharide is sucrose.
Polysaccharides:It's the long polymer chains made up of simple sugar monomers, or complex carbohydrate.
Starch: It is one of the polysaccharide that's found in plant cells that consists entirely of glucose monomers.
Glycogen:It's the way animals store sugare in the form of a polysaccharide, like plant do with starch
Cellulose:It's one of the some polysaccharide that's in plants, serve as building materials,and people nor animal can't digest cellouse




